System Restore Windows 11: 7 Powerful Steps to Recover
Ever had your PC act up after a bad update or install? Don’t panic—System Restore in Windows 11 has your back.
1. Understanding System Restore in Windows 11

System Restore is a built-in Windows feature that allows users to roll back their system files and settings to a previous state without affecting personal data. This is especially useful when troubleshooting issues caused by software changes.
What Is System Restore?
System Restore is a recovery tool that creates snapshots of your system configuration, known as restore points. These restore points can be used to revert your system to a state before a problem occurred.
- Preserves personal files
- Reverts system settings and installed applications
- Useful after driver updates or software installations
“System Restore is one of the most effective troubleshooting tools in Windows.” – Microsoft Docs
How It Works
System Restore monitors system changes and automatically creates restore points before significant events like driver installations, Windows updates, or app installations. Users can also manually create restore points.
- Automatic restore points before major changes
- Manual restore points for added safety
- Does not delete documents or photos
Limitations and What It Doesn’t Do
While powerful, System Restore is not a complete backup solution. It won’t protect against hardware failure or restore deleted personal files.
- Not a substitute for full backups
- Doesn’t affect user-created files
- Won’t fix hardware problems
2. Enabling System Restore in Windows 11
Before using System Restore, it must be enabled. Windows 11 often disables it by default to save system resources.
Checking System Restore Status
To check if System Restore is enabled:
- Open Start Menu and search for “Create a restore point”
- Select the System Protection tab
- Check if protection is turned on for your system drive
Enabling System Restore Manually
If it’s disabled, follow these steps:
- Select your system drive (usually C:)
- Click “Configure”
- Select “Turn on system protection”
- Adjust disk space usage for restore points
- Click “Apply” and then “OK”
Choosing the Right Drive
System Restore should be enabled only for the drive where Windows is installed. Enabling it on other drives is typically unnecessary unless you install critical apps elsewhere.
- Enable only on system drive
- Optional for secondary drives
- Conserves disk space
3. Creating Restore Points
Restore points can be created automatically or manually. It’s a good habit to create one before making significant changes to your system.
Automatic Restore Points
Windows 11 creates restore points automatically before major updates or driver installations.
- Triggered by system events
- Stored in allocated disk space
- Overwritten as new points are created
Manual Restore Points
To create a restore point manually:
- Open “System Properties”
- Click “Create” under the System Protection tab
- Name your restore point descriptively
- Click “Create” and wait for confirmation
Best Practices for Restore Points
Keep your restore points manageable:
- Create before installing new software or drivers
- Limit frequency to avoid disk space issues
- Delete old restore points if needed
4. Performing a System Restore in Windows 11
When your system starts acting up, using a restore point can get things back on track.
Accessing System Restore
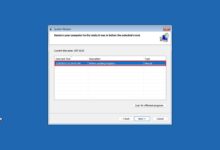
To start a restore:
- Search “Recovery” in the Start menu
- Select “Open System Restore”
- Choose a restore point and follow the prompts
Using Safe Mode
If Windows won’t boot normally, use Safe Mode:
- Press F8 or Shift + Restart
- Select “Advanced Options” > “System Restore”
- Follow the wizard to select a restore point
Restoration Process
Once initiated, System Restore will:
- Restart your PC
- Apply changes
- Notify you upon completion
5. Troubleshooting System Restore Issues
Sometimes, System Restore may fail or not work as expected. Here’s how to troubleshoot.
Restore Point Missing
If restore points disappear:
- Check if System Protection is enabled
- Ensure sufficient disk space
- Look for third-party cleanup tools deleting them
Restore Failed to Complete
Common error messages include:
- “System Restore did not complete successfully”
- “An unspecified error occurred”
Fixes:
- Try Safe Mode
- Disable antivirus temporarily
- Run System File Checker (sfc /scannow)
Alternative Repair Options
If System Restore keeps failing:
- Use Windows Recovery Environment
- Perform a reset or repair install
- Use third-party backup tools
6. Comparing System Restore with Other Recovery Options
Windows 11 offers several recovery tools. Know when to use each.
System Restore vs. Reset This PC
System Restore:
- Non-destructive
- Preserves personal files
- Faster
Reset This PC:
- Reinstalls Windows
- Can remove files or keep them
- More thorough
System Restore vs. File History
File History backs up personal files, not system files. Use both together for full protection.
- System Restore = System settings
- File History = Personal files
System Restore vs. Backup and Restore (Windows 7)
Backup and Restore provides full system images. It’s more comprehensive but slower and uses more space.
- System Restore = Quick fixes
- System Image = Full recovery
7. Advanced Tips for Power Users
Take your System Restore usage to the next level with these pro tips.
Using Command Line
Advanced users can trigger System Restore via Command Prompt:
- Open CMD as Admin
- Use
rstrui.exeto launch the wizard
Restoring from Recovery Environment
If your PC won’t boot:
- Boot from Windows 11 installation media
- Choose “Repair your computer”
- Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > System Restore
Monitoring and Managing Restore Points
Use PowerShell to list and delete restore points:
- Get-ComputerRestorePoint
- Enable-ComputerRestore
- Checkpoint-Computer -Description “My Restore Point”
Frequently Asked Questions
What does System Restore do in Windows 11?
It reverts system settings and files to a previous state without affecting personal data.
Will System Restore delete my files?
No, it only affects system files and settings, not your personal documents or photos.
How long does a system restore take?
Usually between 15 to 45 minutes, depending on your system and the restore point.
Can I undo a system restore?
Yes, Windows 11 allows you to undo the last restore if it didn’t resolve your issue.
Is System Restore enabled by default?
Not always. You may need to enable it manually in System Protection settings.
System Restore in Windows 11 is a powerful tool that can save your system from software mishaps without losing your personal files. By understanding how it works and using it wisely, you can keep your PC stable and secure.
Further Reading: